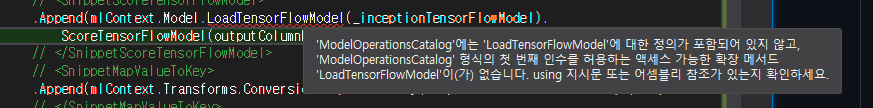
원인
Microsoft.ML.TensorFlow 패키지가 설치되지 않아서 발생한 문제.
해결책
- 도구 > Nuget 패키지 관리자 > 솔루션용 Nuget 패키기 관리... 클릭
- 찾아보기 탭에서 Microsoft.ML.TensorFlow 검색
- 최신버전 설치

Microsoft.ML.TensorFlow 패키지가 설치되지 않아서 발생한 문제.

Microsoft.ML.ImageAnalytics 패키지가 설치되지 않아서 발생한 문제.
Bitmap을 byte[]로 변환하는 방법.
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 42):
* <ggkids9211@gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return Hyunjun Kim.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
byte[] ConvertBitmapToByteArray(Bitmap bitmap)
{
byte[] result = null;
if(bitmap != null)
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
bitmap.Save(stream, bitmap.RawFormat);
result = stream.ToArray();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Bitmap is null.");
}
return result;
}
연산자란 연산 대상이 되는 피연산자에 대한 연산을 수행하는 기호를 뜻한다.
C++에서 사용 가능한 연산자에는 산술 연산자, 관계 연산자, 논리 연산자, 증감 연산자, 대입 연산자, 그리고 비트 연산자가 있다.
산술 연산자는 사칙연산의 연산자들과 나머지 연산자가 있다.
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 |
| + | 덧셈 |
| - | 뺄셈 |
| * | 곱셈 |
| / | 나눗셈 |
| % | 나머지 |
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 42):
* <ggkids9211@gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return Hyunjun Kim.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int b = 2;
int sum = a + b; //더하기
int sub = a - b; //빼기
int mul = a * b; //곱하기
int div = a / b; //나누기
int rem = a % b; //나머지
cout << "sum: " << sum << endl;
cout << "sub: " << sub << endl;
cout << "mul: " << mul << endl;
cout << "div: " << div << endl;
cout << "rem: " << rem << endl;
}
결과
sum: 7
sub: 3
mul: 10
div: 2
rem: 1
산술연산자가 연이어 사용되는 경우에는 아래와 같이 연산 우선순위를 적용한다.
1. 괄호 안의 연산자가 첫번째 우선순위를 가진다.
2. 곱셈, 나눗셈, 나머지 연산자가 그 다음 우선순위를 가진다.
3. 덧셈, 뺄셈 연산자가 그 다음 우선순위를 가진다.
4. 같은 우선순위의 연산자가 나열된 경우 좌측 연산자부터 먼저 처리한다.
관계 연산자는 두 수를 비교하는 연산자이다.
주로 제어문에서 조건을 검사하기위해 많이 사용되며 true 혹은 false를 출력한다.
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 |
| == | 같다 |
| != | 다르다 |
| > | 크다 |
| >= | 크거나 같다 |
| < | 작다 |
| <= | 작거나 같다 |
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 42):
* <ggkids9211@gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return Hyunjun Kim.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int b = 2;
bool same = a == b; //같다
bool diff = a != b; //다르다
bool big = a > b; //크다
bool big_or_same = a >= b; //크거나 같다
bool small = a < b; //작다
bool small_or_same = a <= b; //작거나 같다
cout << "same: " << boolalpha << same << endl;
cout << "diff: " << boolalpha << diff << endl;
cout << "big: " << boolalpha << big << endl;
cout << "big_or_same: " << boolalpha << big_or_same << endl;
cout << "small: " << boolalpha << small << endl;
cout << "small_or_same: " << boolalpha << small_or_same << endl;
}
결과
same: false
diff: true
big: true
big_or_same: true
small: false
small_or_same: false
논리 연산자는 And, Or, Not의 세가지 종류가 있다.
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 |
| && | 그리고 (AND) |
| || | 혹은 (OR) |
| ! | 아닐때 (NOT) |
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 42):
* <ggkids9211@gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return Hyunjun Kim.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
bool AND = true && false;
bool OR = true || false;
bool excl = !true;
cout << "AND: " << boolalpha << AND << endl;
cout << "OR: " << boolalpha << OR << endl;
cout << "excl: " << boolalpha << excl << endl;
}
결과
AND: false
OR: true
excl: false
증감 연산자는 변수의 값을 증가시키거나 감소시킬때 사용한다.
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 |
| ++i | 연산 전에 i값 1 증가 |
| i++ | 연산 후에 i값 1 증가 |
| --i | 연산 전에 i값 1 감소 |
| i-- | 연산 후에 i값 1 감소 |
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* "THE BEER-WARE LICENSE" (Revision 42):
* <ggkids9211@gmail.com> wrote this file. As long as you retain this notice you
* can do whatever you want with this stuff. If we meet some day, and you think
* this stuff is worth it, you can buy me a beer in return Hyunjun Kim.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 9;
cout << "i++: " << i++ << endl; //해당 연산 후에 값 증가
cout << "i: " << i << endl; //연산 이후에 값이 증가함.
i = 9;
cout << "++i: " << ++i << endl; //해당 연산 전에 값 증가됨.
i = 9;
cout << "i--: " << i-- << endl; //해당 연산 후에 값 감소
cout << "i: " << i << endl; //연산 이후에 값이 감소함.
i = 9;
cout << "--i: " << --i << endl; //해당 연산 전에 값 감소됨.
}
결과
i++: 9
i: 10
++i: 10
i--: 9
i: 8
--i: 8
대입 연산자는 동일한 변수가 연산자의 좌우에 모두 쓰이는 경우 간단하게 쓰기위해 사용하는 연산자를 말한다.
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 |
| += | i += j; (이 식과 동일: i = i + j) |
| -= | i -= j; (이 식과 동일: i = i - j) |
| *= | i *= j; (이 식과 동일: i = i * j) |
| /= | i /= j; (이 식과 동일: i = i / j) |
| %= | i %= j; (이 식과 동일: i = i % j) |
비트 연산자는 정수형 데이터의 비트를 직접 제어하는데 사용하는 연산자를 말한다..
각 연산자의 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 정의 | 설명 |
| | | OR | 대응 비트가 하나만 1이어도 1을 출력 |
| ^ | XOR | 대응 비트가 서로 다를 때 1을 출력 |
| << | left shift | 지정된 수만큼 비트들을 왼쪽으로 이동시킴 |
| >> | right shift | 지정된 수만큼 비트들을 오른쪽으로 이동시킴 |
| ~ | 1의 보수 | 0비트는 1로, 1비트는 0으로 변환 |
| [C++] 객체지향 언어 (0) | 2021.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 객체지향의 개념 (0) | 2021.12.01 |
| [C++] 데이터 타입 (0) | 2020.04.25 |
C++에서 사용 가능한 데이터 타입은 정수형, 실수형, 문자형, 그리고 논리형이 있다.
각 데이터 타입은 상수 혹은 변수형태로 표현이 가능하다.
상수는 값이 변경되지 않는 데이터를 말하며 변수는 상황에 따라 변하는 데이터를 말한다.
그럼 기본적인 자료형의 종류를 알아보자
정수형 데이터타입은 크게 세가지로 이루어져있다.
short, int, long타입이다. 각 타입은 하나의 정수를 저장하기 위한 기억공간의 크기로 구분되는데, 통상 int 타입을 기준으로 short 타입은 int 타입의 반이, 그리고 int 타입은 long 타입의 반이 할당된 공간이 주어진다.
ex)
int a;
short b;
long c;
해당 타입들에는 타입 앞에 unsigned란 예약어를 붙일 수 있다.
unsigned는 말 그대로 부호가 붙지 않은 정수. 즉, 양수만을 저장하는 변수를 선언할 때 사용된다. 이는 각 변수별로 할당된 공간을 양수로써 최대로 활용하고자 함에 있다.
각 변수의 데이터 범위 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 크기 | 데이터 범위 |
| short | 2 | |
| unsigned short | 2 | |
| int | 4 | |
| unsigned int | 4 | |
| long | 8 | |
| unsigned long | 8 |
주의해야할 점은 변수를 정의하고 사용할 때는 그 변수에 저장될 값의 범위에 맞게 데이터 타입을 정해주어야한다.
실수형 데이터는 소수점을 가지고 있는 수치 데이터이다. 이 실수형은 두가지로 이루어진다.
float, double 타입이다. float형 데이터는 4바이트, double형 데이터는 8바이트의 공간이 할당된다.
각 변수의 데이터 범위 정의는 다음과 같다.
| 유형 | 크기 | 데이터 범위 |
| float | 4 | |
| double | 8 |
문자형 데이터는 영문자, 숫자, 특수 문자 등을 표현하는 데이터이다.
문자형 데이터 타입은 한쌍의 단일 따옴표를 이용하여 표기하고 문자열 데이터 타입은 이중 따옴표를 이용하여 표기한다.
| 유형 | 크기 | 데이터 범위 |
| char | 1 | |
| unsigned char | 1 | |
| wchar_t | 2 |
C++에서는 특수문자를 사용하여 출력 상태를 제어할 수 있다.
특수문자는 다음과 같다.
| 확장 문자 | 뜻 |
| \n | 줄을 바꾼다. |
| \t | 수평 탭으로 일정 간격을 벌린다. |
| \b | 백스페이스. |
| \r | 같은 줄의 맨 앞으로 커서를 옮긴다. |
| \f | 출력 용지를 한 장 넘긴다. |
| \a | 경고음을 낸다. |
| \/ | / 문자를 출력한다. |
| \' | ' 문자를 출력한다. |
| \" | " 문자를 출력한다. |
| \0 | 널(Null) 문자. |
논리형 데이터 타입은 참, 거짓을 표현하는 데이터이다.
| 유형 | 크기 | 데이터 범위 |
| bool | 1 |
| [C++] 객체지향 언어 (0) | 2021.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 객체지향의 개념 (0) | 2021.12.01 |
| [C++] 연산자 (0) | 2020.04.29 |
3D 오브젝트의 Material 색을 변화시키고 싶을 때 아래 코드를 사용한다.
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestRenderer : MonoBehaviour {
public Renderer m_Renderer;
float m_R = 0.4f;
float m_G = 0.5f;
float m_B = 0.3f;
float m_Alpha = 1f;
void Start(){
m_Renderer.material.color = new Color(m_R, m_G, m_B, m_Alpha);
}
void Update(){
}
}
| [Unity] Unity를 관리자권한으로 켜기. (0) | 2022.01.27 |
|---|---|
| [유니티 입문] 타이머 사용하기 (0) | 2018.06.28 |
| [유니티 입문] Dropdown 사용하기 (2) | 2018.06.28 |
| [유니티입문] 스크립트에서 오브젝트만들기 (2) | 2017.01.18 |
영상처리 프로젝트를 진행하기 시작하면서 단순 CPU만 사용하는 프로그래밍에 한계를 체감하기 시작했다.
기본적으로 1280x720 픽셀데이터를 다루는데만 한번 모든 픽셀을 훓는데만 921,600번의 연산이 필요하고 여기에 갖가지 영상처리 알고리즘이 들어가면 기하급수적인 연산이 걸린다. 각 연산은 단순 사칙연산인 경우가 많으나 연산이 너무 많으니 한번 프로그램을 돌리면 짧게는 몇분, 길게는 몇십분씩 연산이 돌아가니 점점 머리가 미쳐가기 시작했다.
이 많은 연산을 해결하기 위해 우리의 위대한 선조들은 이미 그래픽카드를 개발했고 이 그래픽카드의 GPU속 100코어가 넘는 코어들을 이용해 수많은 계산을 병렬처리로 연산하면서 심하게 오래걸리는 연산들을 단 몇초, 몇 밀리초 안에 해결하도록 솔루션을 내 놓았다.
최근 다양한 GPU Acceleration을 찾아보던 중 익숙한 C#으로 다룰 수 있는 OpenCL 라이브러리를 사용해 GPU Acceleration을 사용해보기로 했다.
먼저 라이브러리를 받아야 하므로 아래 링크에서 가입하거나 로그인해서 라이브러리를 받자.
https://www.codeproject.com/KB/dotnet/1116907/OpenCLLib.zip
비주얼 스튜디오에 DLL 파일을 참조할 수 있는 사람들은 패스하시고 못하시는 분은 아래글을 따라 참조한다.
1. '솔루션 탐색기'에서 '참조'를 오른쪽 클릭 후 '참조 추가'를 누른다.
2. 새로이 뜨는 '참조 관리자'창 우측 하단의 '찾아보기(B)'를 클릭 후 넣고자 하는 라이브러리.dll의 경로를 찾아 '추가'한다.(여기서는 OpenCLlib.dll과 Cloo.dll이다.)
'참조 관리자' 창 내에 추가된 라이브러리의 좌측 체크박스를 체크한다.
이후 '확인' 버튼을 클릭한다.
이렇게 추가한 후 코드 상단에
using OpenCL;
을 추가하여 사용한다.
코드 예제 (소수를 찾는 예제.)
Accord.NET framework은 171가지의 이미지 필터링을 제공하고 있으며 그 목록은 다음과 같다.
| Class | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| AdaptiveSmoothing | Adaptive Smoothing - noise removal with edges preserving. | |
| Add | Add fillter - add pixel values of two images. | |
| AdditiveNoise | Additive noise filter. | |
| ApplyMask | Apply mask to the specified image. | |
| BackwardQuadrilateralTransformation | Performs backward quadrilateral transformation into an area in destination image. | |
| BaseFilter | Base class for filters, which produce new image of the same size as a result of image processing. | |
| BaseFilter2 | Base class for filters, which operate with two images of the same size and format and produce new image as a result. | |
| BaseInPlaceFilter | Base class for filters, which may be applied directly to the source image. | |
| BaseInPlaceFilter2 | Base class for filters, which operate with two images of the same size and format and may be applied directly to the source image. | |
| BaseInPlacePartialFilter | Base class for filters, which may be applied directly to the source image or its part. | |
| BaseResizeFilter | Base class for image resizing filters. | |
| BaseRotateFilter | Base class for image rotation filters. | |
| BaseTransformationFilter | Base class for filters, which may produce new image of different size as a result of image processing. | |
| BaseUsingCopyPartialFilter | Base class for filters, which require source image backup to make them applicable to source image (or its part) directly. | |
| BayerDithering | Ordered dithering using Bayer matrix. | |
| BayerFilter | Generic Bayer fileter image processing routine. | |
| BayerFilterOptimized | Optimized Bayer fileter image processing routine. | |
| BilateralSmoothing | Bilateral filter implementation - edge preserving smoothing and noise reduction that uses chromatic and spatial factors. | |
| BinaryDilation3x3 | Binary dilation operator from Mathematical Morphology with 3x3 structuring element. | |
| BinaryErosion3x3 | Binary erosion operator from Mathematical Morphology with 3x3 structuring element. | |
| BinaryWatershed | Watershed filter. | |
| Blend | Linear Gradient Blending filter. | |
| BlobsFiltering | Blobs filtering by size. | |
| Blur | Blur filter. | |
| BottomHat | Bottop-hat operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| BradleyLocalThresholding | Adaptive thresholding using the internal image. | |
| BrightnessCorrection | Brightness adjusting in RGB color space. | |
| BurkesDithering | Dithering using Burkes error diffusion. | |
| CannyEdgeDetector | Canny edge detector. | |
| CanvasCrop | Fill areas outiside of specified region. | |
| CanvasFill | Fill areas iniside of the specified region. | |
| CanvasMove | Move canvas to the specified point. | |
| ChannelFiltering | Channels filters. | |
| Closing | Closing operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| ColorFiltering | Color filtering. | |
| ColorRemapping | Color remapping. | |
| CombineChannel | Combine channel filter. | |
| CompassConvolution | Compass convolution filter. | |
| Concatenate | Concatenation filter. | |
| ConnectedComponentsLabeling | Connected components labeling. | |
| ConservativeSmoothing | Conservative smoothing. | |
| ContrastCorrection | Contrast adjusting in RGB color space. | |
| ContrastStretch | Contrast stretching filter. | |
| Convolution | Convolution filter. | |
| CornersMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) corners of objects. | |
| Crop | Crop an image. | |
| Difference | Difference filter - get the difference between overlay and source images. | |
| DifferenceEdgeDetector | Difference edge detector. | |
| DifferenceOfGaussians | Difference of Gaussians filter. | |
| Dilation | dilation operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| Dilation3x3 | dilation operator from Mathematical Morphology with 3x3 structuring element. | |
| DistanceTransform | Distance transform filter. | |
| Divide | Divide filter - divide pixel values of two images. | |
| Edges | Simple edge detector. | |
| Erosion | Erosion operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| Erosion3x3 | Erosion operator from Mathematical Morphology with 3x3 structuring element. | |
| ErrorDiffusionDithering | Base class for error diffusion dithering. | |
| ErrorDiffusionToAdjacentNeighbors | Base class for error diffusion dithering, where error is diffused to adjacent neighbor pixels. | |
| EuclideanColorFiltering | Euclidean color filtering. | |
| Exponential | Exponential filter. | |
| ExtractBiggestBlob | Extract the biggest blob from image. | |
| ExtractChannel | Extract RGB channel from image. | |
| ExtractNormalizedRGBChannel | Extract normalized RGB channel from color image. | |
| FastBoxBlur | Fast Box Blur filter. | |
| FastGuidedFilter | Fast Guided Filter (non-commercial). | |
| FastVariance | Fast Variance filter. | |
| FeaturesMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) feature points in a image. | |
| FillHoles | Fill holes in objects in binary image. | |
| FilterIterator | Filter iterator. | |
| FiltersSequence | Filters' collection to apply to an image in sequence. | |
| FlatFieldCorrection | Flat field correction filter. | |
| FloydSteinbergDithering | Dithering using Floyd-Steinberg error diffusion. | |
| GaborFilter | Gabor filter. | |
| GammaCorrection | Gamma correction filter. | |
| GaussianBlur | Gaussian blur filter. | |
| GaussianSharpen | Gaussian sharpen filter. | |
| Grayscale | Base class for image grayscaling. | |
| Grayscale.CommonAlgorithms | Set of predefined common grayscaling algorithms, which have already initialized grayscaling coefficients. | |
| GrayscaleBT709 | Obsolete. Grayscale image using BT709 algorithm. | |
| GrayscaleRMY | Obsolete. Grayscale image using R-Y algorithm. | |
| GrayscaleToRGB | Convert grayscale image to RGB. | |
| GrayscaleY | Obsolete. Grayscale image using Y algorithm. | |
| GrayWorld | Gray World filter for color normalization. | |
| HighBoost | High boost filter. | |
| HistogramEqualization | Histogram equalization filter. | |
| HitAndMiss | Hit-And-Miss operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| HomogenityEdgeDetector | Homogenity edge detector. | |
| HorizontalRunLengthSmoothing | Horizontal run length smoothing algorithm. | |
| HSLFiltering | Color filtering in HSL color space. | |
| HSLLinear | Luminance and saturation linear correction. | |
| HueModifier | Hue modifier. | |
| ImageWarp | Image warp effect filter. | |
| Intersect | Intersect filter - get MIN of pixels in two images. | |
| Invert | Invert image. | |
| IterativeThreshold | Iterative threshold search and binarization. | |
| JarvisJudiceNinkeDithering | Dithering using Jarvis, Judice and Ninke error diffusion. | |
| Jitter | Jitter filter. | |
| KirschEdgeDetector | Kirsch's Edge Detector | |
| Kuwahara | Kuwahara filter. | |
| LevelsLinear | Linear correction of RGB channels. | |
| LevelsLinear16bpp | Linear correction of RGB channels for images, which have 16 bpp planes (16 bit gray images or 48/64 bit colour images). | |
| LineMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) lines in a image. | |
| Logarithm | Log filter. | |
| MaskedFilter | Apply filter according to the specified mask. | |
| Mean | Mean filter. | |
| Median | Median filter. | |
| Merge | Merge filter - get MAX of pixels in two images. | |
| Mirror | Mirroring filter. | |
| Morph | Morph filter. | |
| MoveTowards | Move towards filter. | |
| Multiply | Multiply filter - multiply pixel values of two images. | |
| NiblackThreshold | Niblack Threshold. | |
| OilPainting | Oil painting filter. | |
| Opening | Opening operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| OrderedDithering | Binarization with thresholds matrix. | |
| OtsuThreshold | Otsu thresholding. | |
| PairsMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) pairs of points in a image. | |
| Pixellate | Pixellate filter. | |
| PointedColorFloodFill | Flood filling with specified color starting from specified point. | |
| PointedMeanFloodFill | Flood filling with mean color starting from specified point. | |
| PointsMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) points in a image. | |
| QuadrilateralTransformation | Performs quadrilateral transformation of an area in a given source image. | |
| QuadrilateralTransformationBilinear | Obsolete. Performs quadrilateral transformation using bilinear algorithm for interpolation. | |
| QuadrilateralTransformationNearestNeighbor | Obsolete. Performs quadrilateral transformation using nearest neighbor algorithm for interpolation. | |
| RectanglesMarker | Filter to mark (highlight) rectangles in a image. | |
| Rectification | Rectification filter for projective transformation. | |
| ReplaceChannel | Replace RGB channel of color imgae. | |
| ResizeBicubic | Resize image using bicubic interpolation algorithm. | |
| ResizeBilinear | Resize image using bilinear interpolation algorithm. | |
| ResizeNearestNeighbor | Resize image using nearest neighbor algorithm. | |
| RGChromacity | RG Chromaticity. | |
| RobinsonEdgeDetector | Robinson's Edge Detector | |
| RotateBicubic | Rotate image using bicubic interpolation. | |
| RotateBilinear | Rotate image using bilinear interpolation. | |
| RotateChannels | Rotate RGB channels. | |
| RotateNearestNeighbor | Rotate image using nearest neighbor algorithm. | |
| SaltAndPepperNoise | Salt and pepper noise. | |
| SaturationCorrection | Saturation adjusting in HSL color space. | |
| SauvolaThreshold | Sauvola Threshold. | |
| Sepia | Sepia filter - old brown photo. | |
| Sharpen | Sharpen filter | |
| Shrink | Shrink an image by removing specified color from its boundaries. | |
| SierraDithering | Dithering using Sierra error diffusion. | |
| SimplePosterization | Simple posterization of an image. | |
| SimpleQuadrilateralTransformation | Performs quadrilateral transformation of an area in the source image. | |
| SimpleSkeletonization | Simple skeletonization filter. | |
| SISThreshold | Threshold using Simple Image Statistics (SIS). | |
| SobelEdgeDetector | Sobel edge detector. | |
| StereoAnaglyph | Stereo anaglyph filter. | |
| StuckiDithering | Dithering using Stucki error diffusion. | |
| Subtract | Subtract filter - subtract pixel values of two images. | |
| TexturedFilter | Textured filter - filter an image using texture. | |
| TexturedMerge | Merge two images using factors from texture. | |
| Texturer | Texturer filter. | |
| Threshold | Threshold binarization. | |
| ThresholdedDifference | Calculate difference between two images and threshold it. | |
| ThresholdedEuclideanDifference | Calculate Euclidean difference between two images and threshold it. | |
| ThresholdWithCarry | Threshold binarization with error carry. | |
| TopHat | Top-hat operator from Mathematical Morphology. | |
| TransformFromPolar | Transform polar image into rectangle. | |
| TransformToPolar | Transform rectangle image into circle (to polar coordinates). | |
| Variance | Variance filter. | |
| VerticalRunLengthSmoothing | Vertical run length smoothing algorithm. | |
| WaterWave | Simple water wave effect filter. | |
| WaveletTransform | Wavelet transform filter. | |
| WhitePatch | White Patch filter for color normalization. | |
| WolfJolionThreshold | Wolf Jolion Threshold. | |
| YCbCrExtractChannel | Extract YCbCr channel from image. | |
| YCbCrFiltering | Color filtering in YCbCr color space. | |
| YCbCrLinear | Linear correction of YCbCr channels. | |
| YCbCrReplaceChannel | Replace channel of YCbCr color space. | |
| ZhangSuenSkeletonization | Zhang-Suen skeletonization filter. |
이 필터들은 .NET Standard 2.0 과 .NET Core 2.0 에 완벽하게 호환 제공되고 있다.
이 필터들을 사용하기 위해서는 단순히
using Accord.Imaging.Filters;
을 네임스페이스 위에 삽입하여 사용하면 된다.
예제코드(가우시안 블러 사용 예제)
using System; using System.Drawing; using Accord.Imaging.Filters; using Accord.DataSets; public class Program { public static void Main() { TestImages t = new TestImages(); Bitmap baboon = t.GetImage("baboon.bmp"); // We can create a new Gaussian Blur: GaussianBlur blur = new GaussianBlur(); // Now we can either apply it to the image, creating a // new resulting image to hold the output of the filter: Bitmap result = blur.Apply(baboon); // Or we can apply the operation in place, // overwriting the original image: blur.ApplyInPlace(baboon); } }
Accord.NET은 C#으로만 작성된 .NET framework로써 선형 대수학, 수치 최적화, 통계학, 머신러닝, 인공 신경망, 신호 및 영상처리 등을 처리할 수 있으며 Gnu Lesser Public License 을 따른다.
설치는 다음과 같다.
Visual Studio의 프로젝트를 시작한 후 NuGet Package를 열고 아래 인스톨 명령을 실행한다.
PM> Install-Package Accord.MachineLearning
PM> Install-Package Accord.Controls설치가 완료되면 이제 Accord.NET을 쓸 준비가 된 것이다.
예제코드
using Accord.Controls; using Accord.MachineLearning.VectorMachines.Learning; using Accord.Math.Optimization.Losses; using Accord.Statistics; using Accord.Statistics.Kernels; using System; namespace GettingStarted { class Program { [MTAThread] static void Main(string[] args) { double[][] inputs = { /* 1.*/ new double[] { 0, 0 }, /* 2.*/ new double[] { 1, 0 }, /* 3.*/ new double[] { 0, 1 }, /* 4.*/ new double[] { 1, 1 }, }; int[] outputs = { /* 1. 0 xor 0 = 0: */ 0, /* 2. 1 xor 0 = 1: */ 1, /* 3. 0 xor 1 = 1: */ 1, /* 4. 1 xor 1 = 0: */ 0, }; // Create the learning algorithm with the chosen kernel var smo = new SequentialMinimalOptimization<Gaussian>() { Complexity = 100 // Create a hard-margin SVM }; // Use the algorithm to learn the svm var svm = smo.Learn(inputs, outputs); // Compute the machine's answers for the given inputs bool[] prediction = svm.Decide(inputs); // Compute the classification error between the expected // values and the values actually predicted by the machine: double error = new AccuracyLoss(outputs).Loss(prediction); Console.WriteLine("Error: " + error); // Show results on screen ScatterplotBox.Show("Training data", inputs, outputs); ScatterplotBox.Show("SVM results", inputs, prediction.ToZeroOne()); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
유니티의 여러가지 시간 측정 방법중 한가지인 스탑워치 사용하기에 대한 방법이다.
using System.Diagnostics;
using debug = UnityEngine.Debug;
public class TimerScript : MonoBehaviour {
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
float time;
void Start(){
sw.Start();
}
void Update(){
time = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
if(time>5000){
sw.Stop();
debug.Log("Time: "+time);
}
}
| [Unity] Unity를 관리자권한으로 켜기. (0) | 2022.01.27 |
|---|---|
| Renderer Color값 Script에서 변경하기 (0) | 2018.12.11 |
| [유니티 입문] Dropdown 사용하기 (2) | 2018.06.28 |
| [유니티입문] 스크립트에서 오브젝트만들기 (2) | 2017.01.18 |